Publié le 16 Novembre 2016 – Auteur : Coline Mionnet
Historic Drought in Southwestern United States
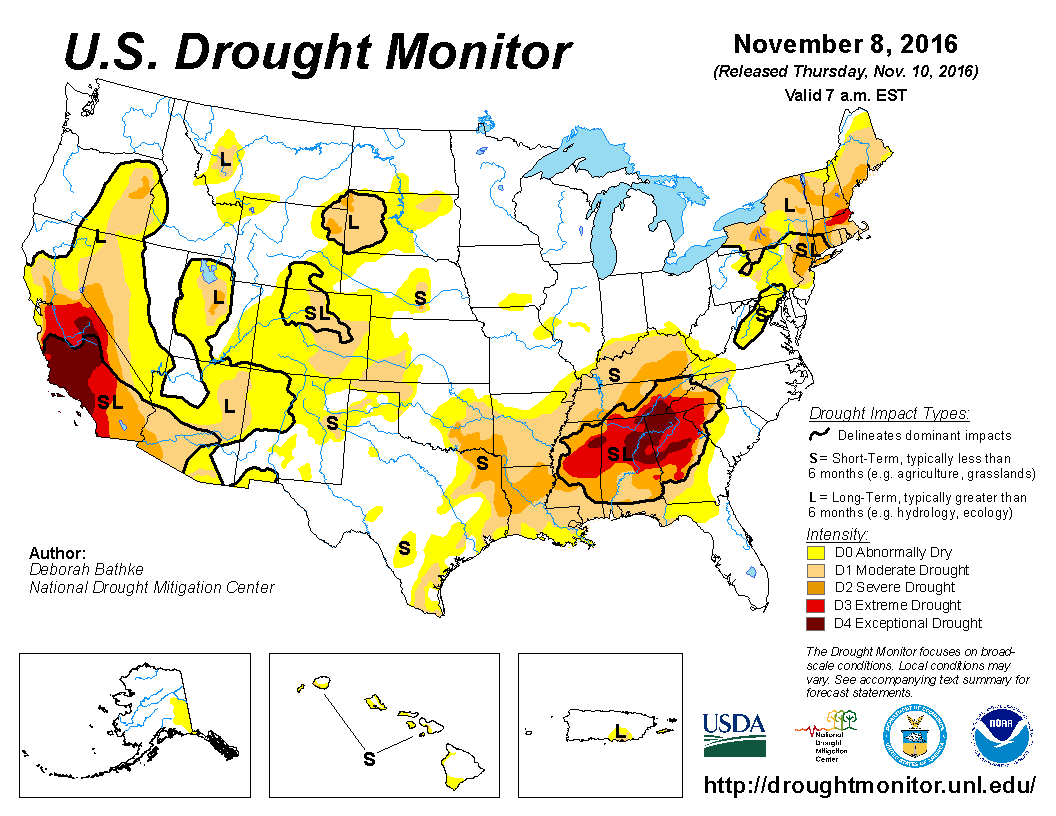
While a horde of climate denizens is preparing to invest in the White House US Southwestern states are experiencing the largest drought ever recorded in more than 40 years.
California and Nevada are the most affected by heat waves and lack of precipitation that have been combined for 5 years in this region but Arizona and Utah are also severely impacted.
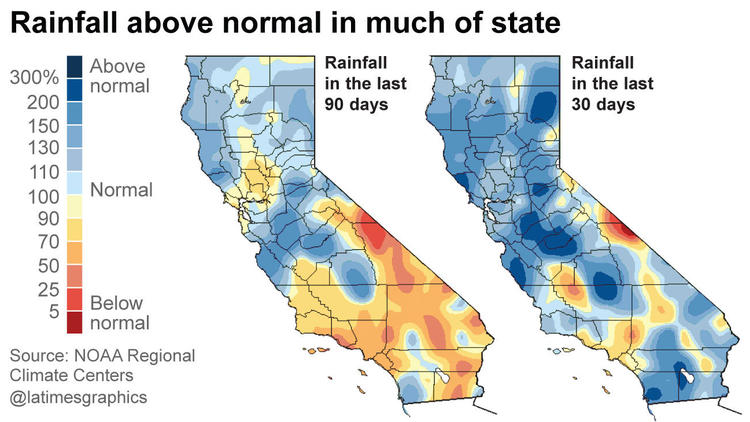
Although the autumn rains have abundantly sprinkled the West Coast for two months, the natural reservoirs supplying drinking water to the big agglomerations are at their lowest. The farmers who have already largely pumped into the water wells are seen today impose restrictions and sometimes destruction of the most demanding crops of water. More than 2000 wells are dry in Great Valley, the agricultural heart of California formed by the Sacramento and San Joaquin valleys, that produce most of the production of almonds apricots figs kiwis grapes and many others
crops very profitable but also very demanding water.
The counterpart of this intensive agriculture is the need to irrigate these crops which would consume nearly 80% of the total water withdrawn in the region.
Most reservoirs in large deficits
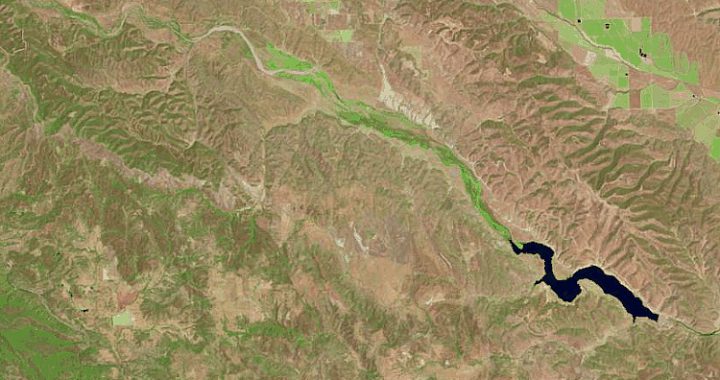
Cachuma Lake which supplies Santa Barbara with drinking water has seen its capacity reduced to 7% as shown by these satellite pictures taken 15 years apart.
Lake San Antonio has not been spared and its leisure park, highly appreciated by the Californians, had to be closed in 2015, its level having collapsed at 4% of its average capacity.That which had not happened since 1967; It was reopened for the summer of 2016.
Neither le New Melones Lake:
This video (YouTube) from 2014 shows the importance of drought.
This YouTube video shows the differences between 2011 and 2014 on the levels of several California lakes.
This catastrophic situation is reminiscent of the virtual disappearance of the Aral Sea in the 1990s.
This historic drought also causes many serious problems for the environment and the regional economy:
- California has faced this year with an increasing number of forest fires which have threatened and sometimes destroyed many homes but especially hundreds of hectares of natural vegetation. According to the Californian authorities, frequency and importance of these fires, often with natural origin, have been increasing for 10 years.
In western America the duration of the fire season has passed, probably due to global warming, from 5 months in the 1970s to more than 7 months this year. The number of fires destroying more than 40 hectares of forest has increased from an average of 140 in the 1980s to 250 in recent years.(Vidéo MAC ENTERTAINEMENT YouTube) - Intensive groundwater pumping for irrigation and dehumidification of soils results in subsidies,particularly in the San Joaquin agricultural valley, where 18 cm of soil subsidence has been identified by NASA, threatening infrastructure.
- Agricultural production is declining sharply, the value of farms is collapsing due to loss of land value and / or destruction of crops, e.g. uprooting of almond plantations.
California’s agriculture is a $ 44 billion market ; the lack of earnings estimates for 2016 is expected to amount as high than $ 2.2 billion. 420,000 acres of farmland has gone unplanted this year, and a quarter of the rice production, about 140.000 acres, was lost due to extreme drought and water shortage. - Health consequences arise in rural areas due to the poor quality of water available. In some areas residents no longer use tap water for drinking and cooking due to the increased concentration of pollutants as their dillution is reduced by the smaller amount of the resource.
- On the other hand hydroelectric production is affected by the critical level of reservoirs which does not permit normal operation of the power stations in all seasons.
- Lastly the economy of summer tourism around the lakes is strongly impacted by the partial drying of the water bodies which are as many recreational nautical bases. The last winter sports season was very poor, some stations having to open later and close earlier, mainly in Southern California.
Las Vegas, 2 million inhabitants, 40 million tourists
Considered another year ago as "the largest reservoir in the United States ", Mead Lake, which supplies Las Vegas with drinking water, reached a 20-year low in the spring before rising again this fall to its 2015 level.A difference of more than 40 meters from its maximum level for a capacity less than 40%. As for the Hoover dam which operates the artificial lake its electricity production dropped by two-thirds in 2016. Negotiations are underway between California, Nevada and Arizona to adopt a program to reduce water consumption.
At the same time the states of the upstream basin of Colorado, Wyoming and Colorado are considering creating new reservoirs to secure the future of their water supply, which would deprive the downstream states of as much resources.
If winter does not bring rain and snow in substantial quantities, the city of Las Vegas, a part of Nevada and Arizona could experience an extremely tight drinking water supply next year.
“The ski resort industry is facing huge challenges, and at least 150 of the current 470 ski resorts in the United States are going to fail and turn off the lifts.” This pessimistic forecast of Bill Jenssen, an expert of the ski industry in the United States, has thrown a cold in the assembly of the SIA (Snowsports Industries America) trades show, ,meeting in January 2015 nearly two years ago in Denver, Colorado.
According to his analysis 150 of the 470 ski resorts in the United States are condemned in the medium term due to lack of snow, 150 resorts would be called upon to develop and 150 would just survive the consequences of global warming.
As of March 31 2016 rainfall did not reach 60% of an average year and one third of a very good year. In California some stations had to close in late February confirming Bill Jenssen’s forecasts.
En Californie, certaines stations ont du fermer fin février, confirmant les prévisions de Bill Jenssen.
De plus, la saison avait commencé très tard du fait d’un mois de décembre anormalement doux.
To date November 17 2016 not any California station has yet been able to open.

Sources
U.S. Drought Monitor, weekly updated
Las Vegas Going Dry? Largest Reservoir In America Reaches Record Low, ZeroEdge, Jun 17, 2016
Drought on Colorado River sparks revolutionary idea: sharing water, site KQOD Science
Western wildfires and climate change, PDF, Union of Concerned Scientists website
NASA: California Drought Causing Valley Land to Sink
Ski Industry Expert Says 31% of Today’s Ski Areas Are Dying, CURBED SKI website
California Farmers Harvest Smaller Crops Due to Drought, AG Web
It’s Official: This Year’s ‘Super El Niño’ Was a Dud for Southern California, Curbed Ski website
The Latest California Snow Totals & Ski Conditions, On The Snow website, real time
Kettleman water project poised to start, The sentinel, Nov 15, 2016